Table of Contents
- Understanding Large-Scale Building Systems for Education
- Why Rigamajig Building Kit Stands Out
- Educational Benefits of Open-Ended Building Systems
- Implementing the Rigamajig Basic Builder Kit in Your Institution
- Safety and Durability Considerations
- FAQs About Construction-Based Learning
Understanding Large-Scale Building Systems for Education
The rigamajig building kit represents a paradigm shift in how early childhood educators approach STEM learning. Unlike traditional classroom manipulatives that limit children to small-scale creations, these large-format wooden construction systems enable children to build structures they can actually climb inside, push, and physically interact with at a life-size scale.
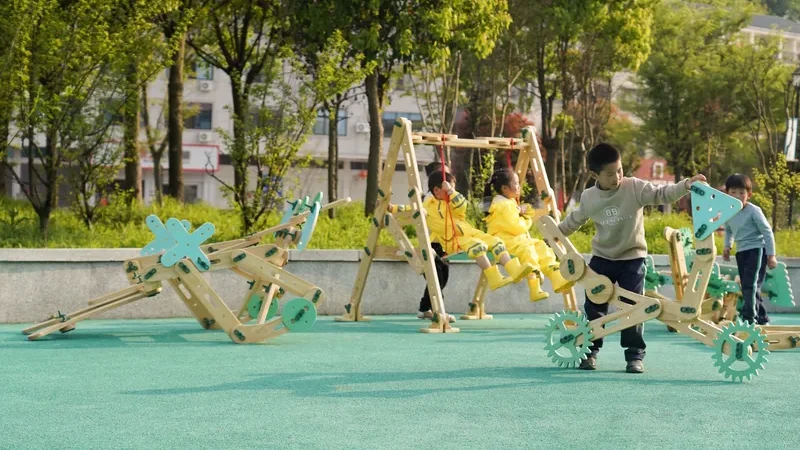
Research from educational institutions worldwide demonstrates that when children engage with building materials at this scale, they develop deeper understanding of engineering principles, spatial reasoning, and collaborative problem-solving skills. The physical engagement required to manipulate larger components also integrates gross motor development with cognitive learning—a powerful combination for comprehensive child development.
What Makes the Rigamajig Approach Unique
The rigamajig toy philosophy centers on three core principles:
Open-Ended Design: No instruction manuals mean children must rely on imagination and problem-solving rather than following predetermined steps. This approach aligns with modern constructivist learning theory that emphasizes active knowledge construction.
Collaborative Scale: Individual pieces are deliberately sized to encourage teamwork. A single child cannot easily complete complex projects alone, naturally fostering communication and shared decision-making.
Real Engineering Components: Unlike simplified toy versions, these systems use actual mechanical elements—pulleys, axles, nuts, and bolts—introducing authentic engineering concepts from an early age.
Why Rigamajig Building Kit Stands Out
When educational institutions evaluate construction-based learning materials, several factors distinguish premium options like the rigamajig building kit from standard alternatives.
Material Quality and Longevity
High-grade Baltic birch plywood forms the foundation of durable educational building systems. This material choice provides several critical advantages for institutional buyers:
- Durability: Withstands years of intensive classroom use
- Safety: Smooth edges and splinter-resistant surfaces
- Sustainability: Responsibly sourced wood from renewable forests
- Aesthetics: Natural wood grain appeals to both children and educators
According to the Sustainable Furnishings Council, wood toys produce significantly lower carbon emissions than plastic alternatives, making them an environmentally conscious choice for forward-thinking educational institutions.
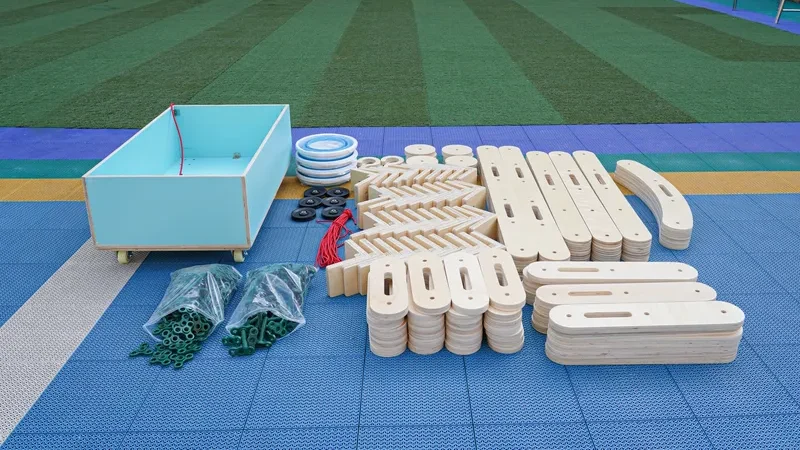

The Rigamajig Basic Builder Kit: Components Breakdown
A comprehensive rigamajig basic builder kit typically includes:
- 265+ pieces including wooden planks of varying lengths
- Wheels and axles for creating mobile constructions
- Pulleys and rope for exploring simple machines
- Child-friendly hardware (wing bolts, nuts, brackets)
- Mobile storage solutions for organized classroom management
This component variety enables countless project possibilities while teaching children to make strategic decisions about which pieces best serve their creative vision.
STEM Learning Integration
The rigamajig building kit naturally integrates all STEM disciplines:
Science: Gravity, force, balance, friction, cause and effect
Technology: Simple and complex machine principles
Engineering: Structural design, problem-solving, iterative testing
Mathematics: Measurement, geometry, spatial relationships, counting
Educational research published by the National Association for the Education of Young Children confirms that integrated STEM experiences create more meaningful learning than isolated subject instruction.
Educational Benefits of Open-Ended Building Systems
The educational impact of implementing a rigamajig building kit in preschools, kindergartens, and elementary classrooms extends far beyond basic construction skills.
Developing 21st Century Skills
Modern employers consistently identify these competencies as essential for future workforce readiness:
Critical Thinking: Children must analyze structural stability, weight distribution, and component relationships. When a tower collapses, they engage in scientific reasoning to understand why and how to improve their design.
Creativity: Without prescribed outcomes, children exercise pure creative thinking. A set of wooden planks becomes a bridge, a castle, a spaceship, or a marketplace depending entirely on their imagination.
Collaboration: Large-scale projects naturally require teamwork. Children practice negotiation, compromise, task distribution, and collective problem-solving—skills that transfer to all areas of life.
Communication: Articulating design ideas, explaining technical solutions, and coordinating group efforts develop both receptive and expressive language skills.
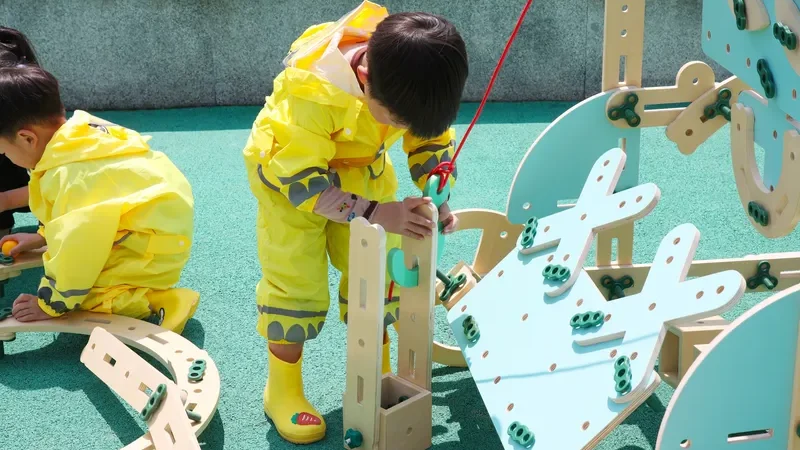

Social-Emotional Learning Through Building
Beyond academics, construction-based learning supports emotional development:
- Frustration tolerance: Projects don’t always work on the first attempt
- Persistence: Children learn to iterate and improve
- Pride in accomplishment: Completing a life-size creation builds confidence
- Empathy: Understanding peers’ ideas and perspectives during collaboration
Physical Development Integration
Manipulating large wooden components provides genuine physical exercise:
- Gross motor skills: Lifting, carrying, positioning planks
- Fine motor skills: Tightening bolts, threading rope, manipulating small hardware
- Hand-eye coordination: Aligning connection points, balancing components
- Body awareness: Working with life-size structures develops spatial understanding
Implementing the Rigamajig Basic Builder Kit in Your Institution
Successfully integrating a rigamajig basic builder kit into your educational program requires thoughtful planning and teacher preparation.
Space Requirements and Setup
Minimum Space: Allocate at least 200 square feet (approximately 18 square meters) for optimal use. This allows multiple children to work simultaneously without crowding.
Flooring Considerations: Rubber mats or carpet tiles cushion falls and reduce noise. Avoid slippery hard surfaces where wheels might cause instability.
Storage Solutions: Dedicated mobile storage carts or workshop displays keep components organized and visible. Children build more complex creations when they can easily see all available pieces.
Teacher Training and Facilitation Strategies
Educators accustomed to structured lesson plans may initially feel uncertain about facilitating open-ended construction. Professional development in this area focuses on:
The Observer Role: Teachers document learning rather than directing it. Photographing constructions, recording children’s explanations, and noting problem-solving strategies creates valuable assessment data.
Strategic Questioning: Instead of providing solutions, teachers ask questions that prompt deeper thinking: “What could make your structure more stable?” “How might you test whether that will work?”
Challenge Introduction: Once children master basic building, teachers can introduce engineering challenges that extend learning while maintaining open-ended exploration.

Curriculum Integration Examples
The versatility of the rigamajig building kit supports integration across subject areas:
Literacy Connection: Children document their constructions through drawings and dictated descriptions. Create a class “Invention Journal” where designs are archived.
Mathematics Application: Measure structure heights, count components used, graph which pieces children use most frequently, or calculate how many planks equal one meter.
Science Investigation: Test which designs hold the most weight, explore ramp angles to move objects, or investigate how pulley systems reduce effort.
Social Studies Exploration: Build community structures (post office, grocery store, fire station) and discuss their purposes. Create models of different cultural architecture styles.
Safety and Durability Considerations
Institutional buyers must prioritize safety while ensuring products withstand intensive use.
Age-Appropriate Design Features
The rigamajig building kit and comparable systems incorporate several safety features specifically for educational settings:
Size Specifications: Pieces large enough to prevent choking hazards while small enough for children to manipulate independently.
Weight Distribution: Individual components light enough for young children to lift safely, but substantial enough to create stable structures.
Connection Mechanisms: Child-friendly wing bolts eliminate pinch points common with traditional bolt and wrench systems. Children develop sufficient hand strength to tighten connections without requiring adult assistance.
Maintenance and Inspection Protocols
Establish regular maintenance schedules to extend product lifespan:
Weekly Checks: Quickly scan for splinters, cracked wood, or missing components. Remove damaged pieces immediately.
Monthly Deep Cleaning: Wipe all wooden surfaces with approved wood-safe cleaners. Inspect hardware for rust or wear.
Quarterly Inventory: Count pieces against original manifest. Order replacement components for lost items to maintain complete sets.
Annual Professional Inspection: Have facilities staff examine all pieces for structural integrity, particularly after heavy use during busy program periods.
Insurance and Liability Considerations
Document your safety protocols when using large-scale construction materials:
- Photograph setup areas showing appropriate spacing and flooring
- Maintain records of safety training for staff
- Keep manufacturer’s safety certifications readily accessible
- Document incident reports (even minor ones) to identify patterns
Consult your institution’s insurance provider about appropriate liability coverage for construction-based learning activities.
FAQs About Construction-Based Learning
What age ranges benefit most from rigamajig building kit activities?
The rigamajig building kit serves children from age 3 through upper elementary years (approximately age 11-12). Younger children focus on basic construction and manipulation, while older students tackle engineering challenges and create complex moving machines. The open-ended nature ensures every developmental level finds appropriate challenge.
How many children can work with one rigamajig basic builder kit simultaneously?
Most comprehensive kits comfortably accommodate 4-8 children working simultaneously, or 2-20 children in a supervised rotation system. The ideal group size depends on whether you’re facilitating structured challenges (smaller groups) or free exploration (larger groups).
Can rigamajig toy systems be used outdoors?
Yes, though outdoor use requires weather considerations. Store wooden components indoors when not in use to prevent water damage and warping. Brief outdoor sessions work well on dry days, but avoid leaving materials exposed to moisture or extreme temperatures.
How do building kits compare to digital STEM learning tools?
Physical construction systems like the rigamajig building kit offer irreplaceable tactile learning experiences. While digital tools teach coding and computational thinking, hands-on building develops spatial reasoning, physical problem-solving, and real-world engineering understanding that screens cannot replicate. The most effective programs integrate both.
What classroom management strategies prevent conflicts during building activities?
Establish clear protocols: designated building areas, maximum group sizes, component sharing expectations, and time limits for popular pieces. Teach specific collaboration skills through modeling and practice. Consider creating role assignments (design lead, materials manager, construction lead) that rotate among group members.
Are there alternatives to rigamajig for budget-conscious programs?
While the Rigamajig brand offers premium quality, several alternatives exist at various price points. Research shows that key factors for educational value include: natural materials (versus plastic), open-ended design, appropriate sizing for collaboration, and sufficient component variety. When comparing alternatives, calculate cost per year based on expected lifespan rather than initial price alone.
Conclusion: Investing in Hands-On STEM Excellence
Educational institutions worldwide recognize that children learn engineering, collaboration, and creative problem-solving most effectively through direct physical experience. The rigamajig building kit and similar large-scale wooden construction systems provide authentic hands-on learning that transforms classrooms into innovation labs where children develop the critical thinking skills that will serve them throughout their lives.
Whether you’re outfitting a new preschool, upgrading kindergarten materials, or seeking to distinguish your educational program with cutting-edge STEM resources, thoughtful investment in quality wooden building systems delivers measurable results. Children don’t just play with these materials—they become engineers, architects, and collaborative innovators, building both structures and the foundational skills for future success.
For educational distributors, curriculum specialists and institutional buyers seeking quality wooden educational toys manufactured to the highest safety and quality standards, discover our full line of architectural learning solutions designed specifically for the international education market.